Nigella Sativa (Black Cumin)
Authors: H Toma, N Hasan, SC Ganguli
Introduction
Nigella sativa (N. sativa) (black-caraway, also known as nigella or kalonji), often called black cumin is found mainly in south and southwest Asia and belongs to the family Ranunculaceae. The black caraway fruit is large with delicate three to seven united follicles with seeds. Nigella Sativa oil and seeds are being investigated because their components have exceptional medicinal properties and have been widely used in various foods and pharmaceutical products.
The seeds and oil is considered as one of the greatest forms of healing medicine also recommended for using in Prophetic Medicine to treat several diseases and ailments. Black cumin has been extensively studied and has many beneficial properties as an antihypertensive, anti- diabetic, diuretics, analgesics and anti-bacterial (2). Thymoquinone, which is the major bioactive component of the essential oil (30%), has the most therapeutic effect . Carvacrol, tanethole, and 4-terpineol are also constituents of the oil and have demonstrated significant radical scavenging activity. (3)
Forms/selection/storage
Nigella sativa can be used in various forms, both whole and as a powder, oil or extract. It can be stored at room temperature however, essential fatty acids are easily destroyed by heat or prolonged exposure to air. For this reason, it is best to store the seeds in a cool dark place or in the fridge. If it starts to give a musty smell it should be thrown away (4) It is easily found online and stocked in small bottles by bigger supermarkets as ‘kalonji’ in spices section and has a very long life if kept cool and dark in an airtight container. There are many supplements available that usually use the basic seed extract or the seed oil and do not require a large degree of processing (10) N. sativa essential oil can be used in a variety of food applications which gives this oil industrial importance. The essential oil showed stronger antioxidant potential and stronger radical scavenging activity against 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl radical compared with synthetic antioxidants. (5)
Commercially produced Nigella seed oil is generally obtained by cold pressing of raw or slightly roasted seeds or by solvent extraction .The pressed oil of N. sativa is used topically to treat skin eruptions, paralysis, back pain, rheumatism, and other inflammatory diseases (6).
Tips for preparing & cooking
Nigella Sativa seeds have been widely used for culinary purposes to add flavor to food and has also been used for toppings on bread and garnish on salads.Toasted and ground Nigella seeds can be used on any dish, In fact, these seeds are used to top flat bread and pastries in Turkey and Middle Eastern countries. The aroma of these toasted and crushed seeds can be described as like lemons; in spicy dishes, their taste changes and blends into the notes of onions and black peppers. It’s better to start cooking with a small quantity of Nigella Seeds first and then tailor the dish according to the taste. Once you are familiar with the taste, it is recommended to dry roast or microwave the seeds before use for an enhanced flavor. The seeds are also used as a whole and for vegetable curries as well. Bengalis also mix these seeds with other spices like mustard seed & fenugreek in their world-famous spice called ‘Paanch-Pooran’ (8).
Nutritional Profile
Nigella Sativa seeds contain crude fibre, minerals (e.g. Fe, Na, Cu, Zn, P and Ca) and vitamins like ascorbic acid, thiamine, niacin, pyridoxine and folic acid . The seed contains fatty acids (e.g. palmitic acid, oleic acid and linoleic acid), terpenoids, aliphatic alcohols and unsaturated hydroxy ketones. Moreover, free sterols, steryl esters, steryl glucosides and acylated steryl glucosides were isolated from the seed oil. A novel alkaloid (nigellicine), an isoquinoline alkaloid (nigellimine) and an indazole alkaloid (nigellidine) were also isolated from the black cumin seeds .The active constituents of the seeds include the volatile oil consisting of carvone, an unsaturated ketone, terpene or d-limonene also called carvene, a-pinene and p-cymene.The crystalline active principle, nigellone, is the only constituent of the carbonyl fraction of the oil. Pharmacologically, active constituents of volatile oil are thymoquinone, dithymoquinone, thymohydroquinon and thymol (9).
Possible Health Benefits
Studies of Nigella Sativa and Blood Pressure
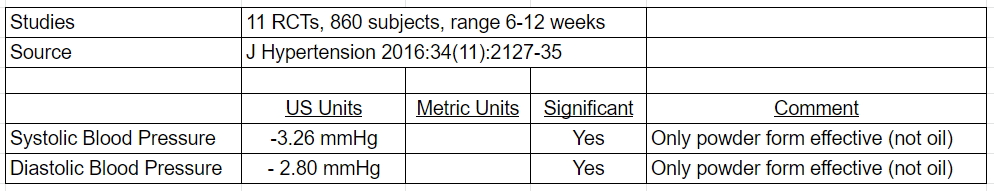
A recent meta-analysis (10) looked at the magnitude of nigella sativa (N sativa) on systolic (SBP) and diastolic (DBP) blood pressure (see table below). While preparations of N Sativa powder demonstrated a statistically significant effect on SBP and DBP, this was not the case for oil. No association was seen between SBP lowering and time on treatment, or N sativa dosage. There was no evidence of any publication bias.
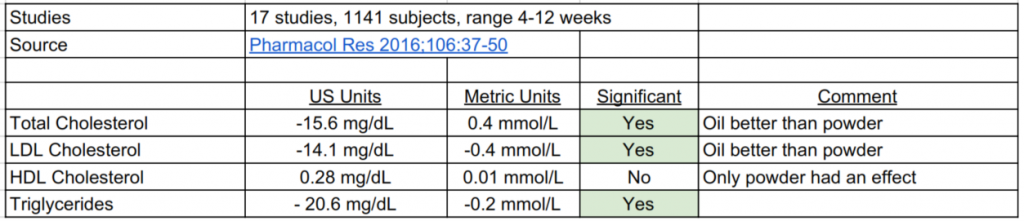
Studies of Nigella Sativa and Blood Lipids
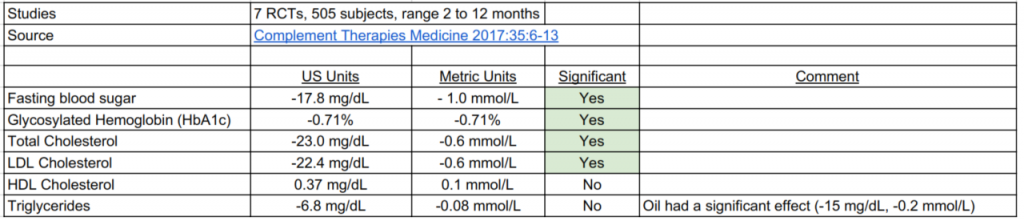
Studies of Nigella Sativa in Diabetics
Studies of Nigella Sativa in Subjects with Obesity
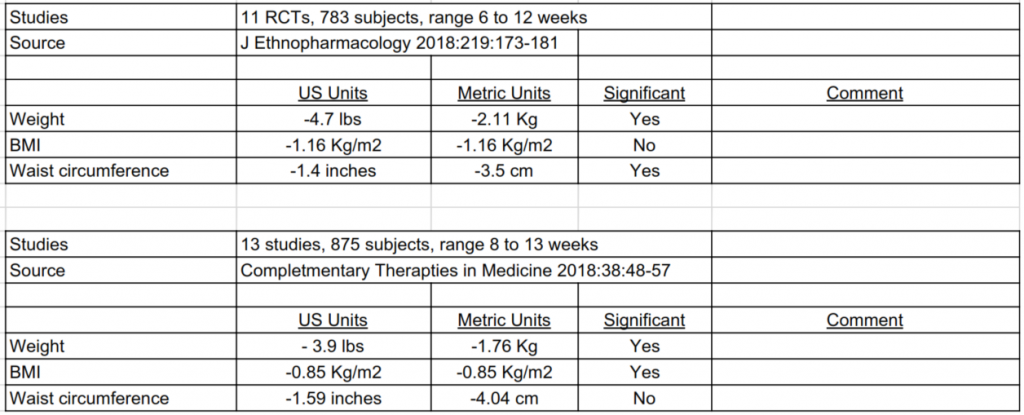
Taken together, these two meta-analyses would suggest that nigella sativa results in weight loss of about 2 Kg (4.5 lbs), a decrease in BMI of about 1 Kg/m2, and a decrease in waist circumference of about 4 cm (1.5 inches).
References
1) Nigella Sativa. Wikipedia 2017
2) Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 2013 May; 3(5): 337-52. A review on therapeutic potential of Nigella sativa: A miracle herb.Ahmad A, Husain A, Mujeeb M, Khan SA, Najmi AK, Siddique NA, Damanhouri ZA, Anwar F.
3)Cardiovasc Toxicol (2013) 13:9–21 DOI 10.1007/s12012-012-9181-zCardiovascular Benefits of Black Cumin (Nigella sativa) Adel Shabana • Ayman El-Menyar • Mohammad Asim • Hiba Al-Azzeh • Hassan Al Thani
4) https://theblessedseed.com/black-seed-oil-care/
5) Essential Oils in Food Preservation, Flavor and Safety. 2016, Pages 269–27
Chapter 30 – Black Cumin (Nigella sativa) Oils.Mohamed F. Ramadan.https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-416641-7.00030-4
6.)Gourmet and Health-Promoting Specialty Oils. 2009, Pages 299–31110– Nigella (Black Cumin) Seed Oil.AfafKamalEldin.https://doi.org/10.1016/B9781-893997-97-4.50016-4
7)Medical Journal of Babylon – 2006 Volume 3 No. 1-2 Hormonal Contents of Two Types of Black Seed (Nigella sativa) Oil: Comparative Study Abdulsamie H. Alta’ee Mufeed J. Ewadh* Haider K. Zaidan
8) Glossary-nigella-seed-https://www.bbcgoodfood.com 2017
9) International Journal of Food Science & Technology (2007). 42. 1208 – 1218. 10.1111/j.1365-2621.2006.01417.x. Nutritional value, functional properties and nutraceutical applications of black cumin (Nigella sativa L.): An overview.Hassanien, Mohamed.
10) J Hypertension 2016:34(11):2127-35 A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials investigating the effects of supplementation with Nigella sativa (black seed) on blood pressure. A Sahebkar et al.