New Liver Disease Patient Page
This page is for patients who have been referred for a consultation by their doctor.
NAFLD (non-alcoholic fatty liver disease) is very common and is a group of conditions in which there is the accumulation of excess fat in the liver of people who drink little or no alcohol. The most common form of NAFLD is called fatty liver and is characterised by the accumulation of fat in liver cells; this does not usually damage the liver or progress to more serious diseases.
A small group of people with NAFLD may have or develop NASH (non-alcoholic steatohepatitis) which is more serious and is associated with liver cell inflammation, scarring and may lead to cirrhosis, liver failure with its complications and need for transplantation, or death.
The majority of individuals with NAFLD have no symptoms and a normal physical examination.
Causes of NAFLD / NASH
NAFLD is also part of the ‘metabolic syndrome’ which is characterized by diabetes or pre-diabetes (insulin resistance), being overweight, elevated blood lipids such as cholesterol and triglycerides, and high blood pressure.
A wide range of diseases and conditions can increase your risk of NAFLD including:
- High cholesterol
- High levels of blood triglycerides
- Obesity
- Type 2 diabetes
While NAFLD patients only have a small risk of chronic liver disease, they also have an increased risk of other diseases:
- There is a 64% increase in the rate of new cardiovascular disease
- The rate of type 2 diabetes (NIDDM) is more than doubled.
- Diabetics with NAFLD have a risk of cardiovascular events more than twice that of diabetics without NAFLD
- Overweight patients with NASH are six times more likely to have chronic kidney disease (25% vs 4%;P<0.001) than overweight patients without NASH.
Multiple studies of the effect of lifestyle and NAFLD have shown that exercise can produce reductions in the amount of fat in the liver and improve liver tests; however the effect is less than that observed with weight reduction.
When fructose (eg pop, high fructose corn syrup) is part of a high calorie diet, one sees an increase in liver fat content and worsening of liver tests. An interesting study of 41 obese children found that restriction of fructose intake for just 9 days resulted in a significant decrease in liver fat (as well as fat elsewhere in the body).
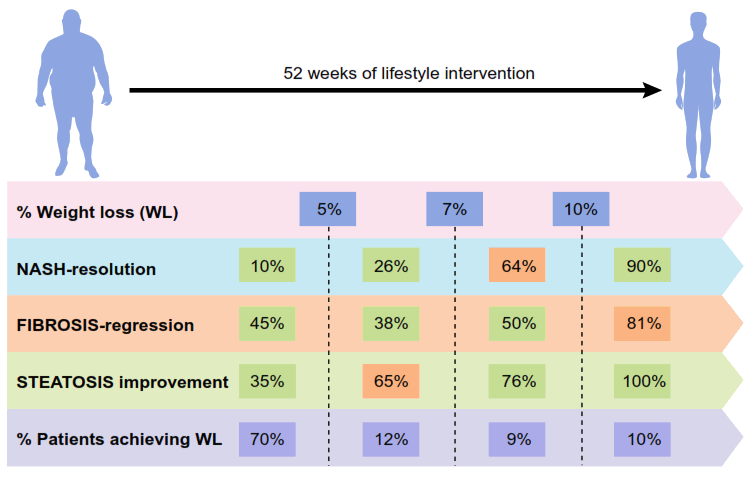
However, the best way to cause NASH and its complications to reverse or resolve is with weight loss as can be seen in the figure below:
As you can see above, small amounts of weight loss can have large results. As the amount of weight loss goes from 5% to 10% of weight one sees the following:
- The rate of resolution of NASH goes from 10% to more than 60%
- Reversal of scarring of the liver (fibrosis) goes from 45% to over 80%
- The improvement of fat in the liver goes from 35% to over 90%.
While most common weight loss diets only achieve small and temporary results, a Whole Food Plant-based Diet can have long-lasting and significant results:
In addition, this type of diet is associated with a greater than 50% decrease in the rate of metabolic syndrome.
In a randomized study of 62 overweight women, a ‘heart healthy’ diet was compared to a Whole Food Plant-based (WFPB) diet over 2 years. At the end of 2 years the results showed that: 1) Subjects following a WFPB diet lost significantly more weight (3.1 vs 0.8 Kg), 2) Those who attended a support group lost significantly more weight than those who did not (3.9 vs 0.4 kg).
In another study from New Zealand (see video below), 65 subjects from the practice of a family doctor were randomized to normal care vs a WFPB diet (which included participation in a support group). After 12 months, the WFPB subjects lost an average of 12.1 kg (25 lbs) which was 12% of their initial weight.
To summarise the main points above:
- Fatty liver disease can lead to liver failure and death and is associated with increased rates of heart disease, diabetes and its complications.
- Weight loss can reverse fatty liver disease and many of its complications
- A Whole Food Plant-based diet is an effective way to lose weight.
It is now clear that the healthiest diet (and the only diet able to reverse heart disease) is a Whole Food Plant-based Diet (WFPB) which is made of Whole (unprocessed) Foods, and is Plant Based (ie no animal products such as meat, chicken, fish, eggs, milk or cheese).
Hopefully, you now understand the value of nutrition in the prevention (and frequently also the treatment) of chronic disease. If you need more information, see this video and my pages on diabetes, heart disease, and cancer and review the rest of this website (overview here).
If you would like to be seen in consultation by Dr Ganguli to help you to adopt a Whole Food Plant-Based (WFPB) diet, please call the number on the sheet of paper you were given by your doctor and leave the requested information so that you can be contacted with an appointment.
While you are waiting to be seen, please review this website and the video below:
Don’t feel bad it took you a while to realize this – here is the touching story of a cardiologist who realised that he had his own health problem and ended up finding a natural solution.
If you need more convincing, see the video below: